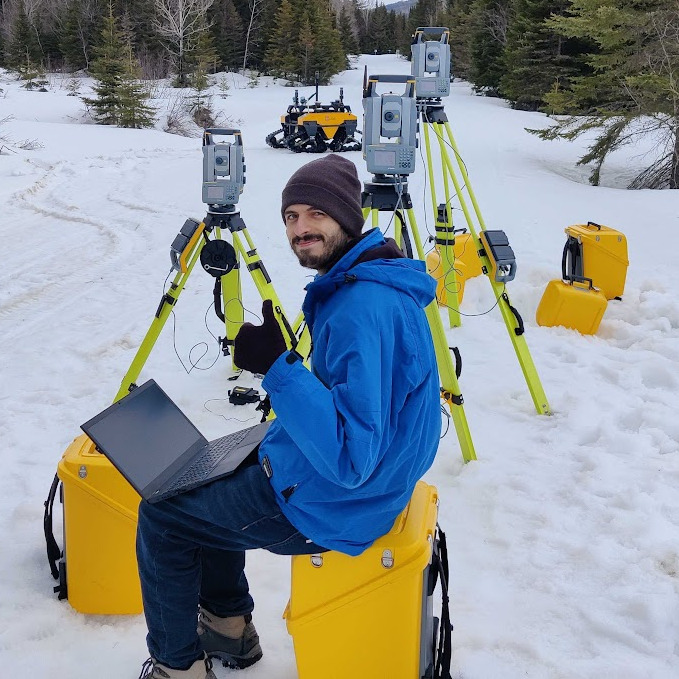

Damien LaRocque
ROSCon FR & DE 2025 highlights
Highlights from Strasbourg

(Le texte en français se trouve ici)
UVT-RS
A blazingly fast trajectory description file format
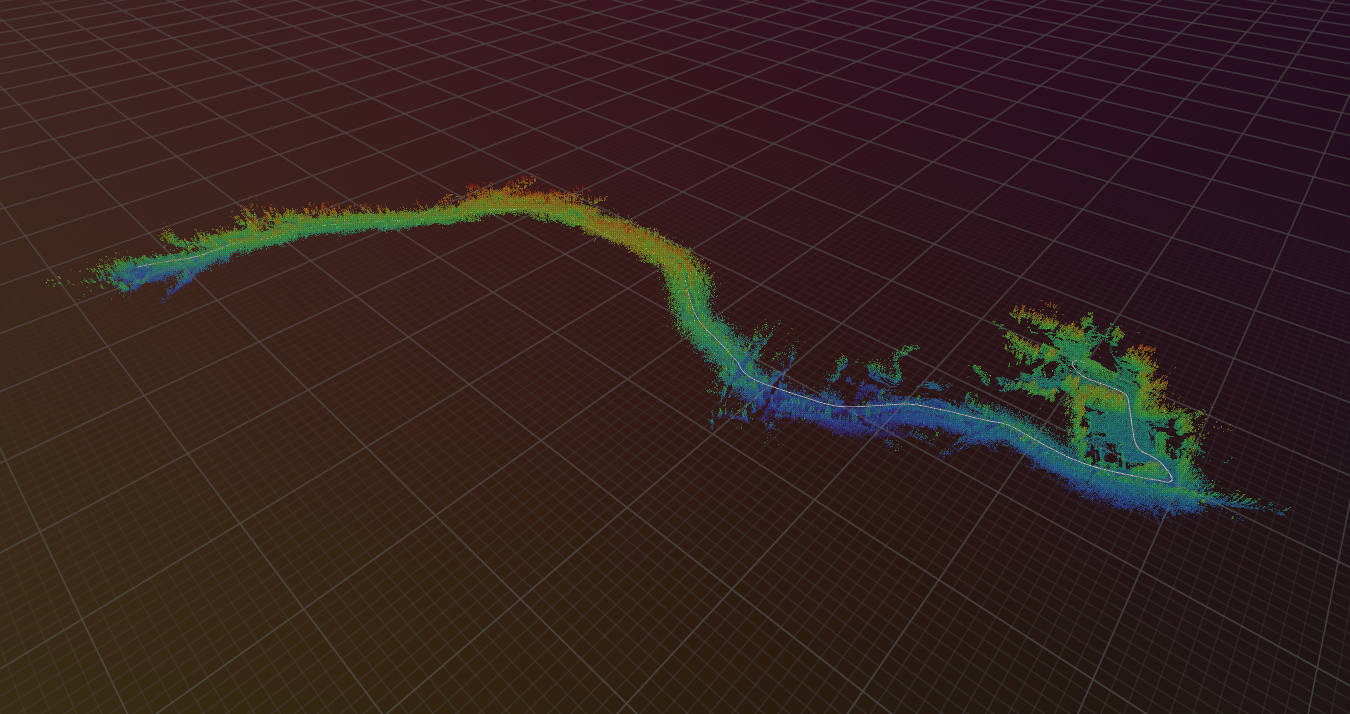
During the last months, I worked on uvt-rs, my first project in Rust 🦀!
uvt-rs is a collection of Rust crates for processing and interacting with Uncrewed Vehicle Trajectory (UVT) files.
The UVT file format provides a lightweight way to describe trajectories of uncrewed vehicles, such as UAV, UGV, etc.
It was designed as an extension of the LTR format introduced in Kilometer-Scale Autonomous Navigation in Subarctic Forests: Challenges and Lessons Learned.
ROS 2 Tips & Tricks
Small configurations for your ROS 2 workflow
Here are a few tips and tricks and configurations to add to your system while working with ROS 2.
Using Citizen Science Data as Pre-Training for Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution UAV Images for Natural Forests Post-Disturbance Assessment
Published in MDPI Forests journal!
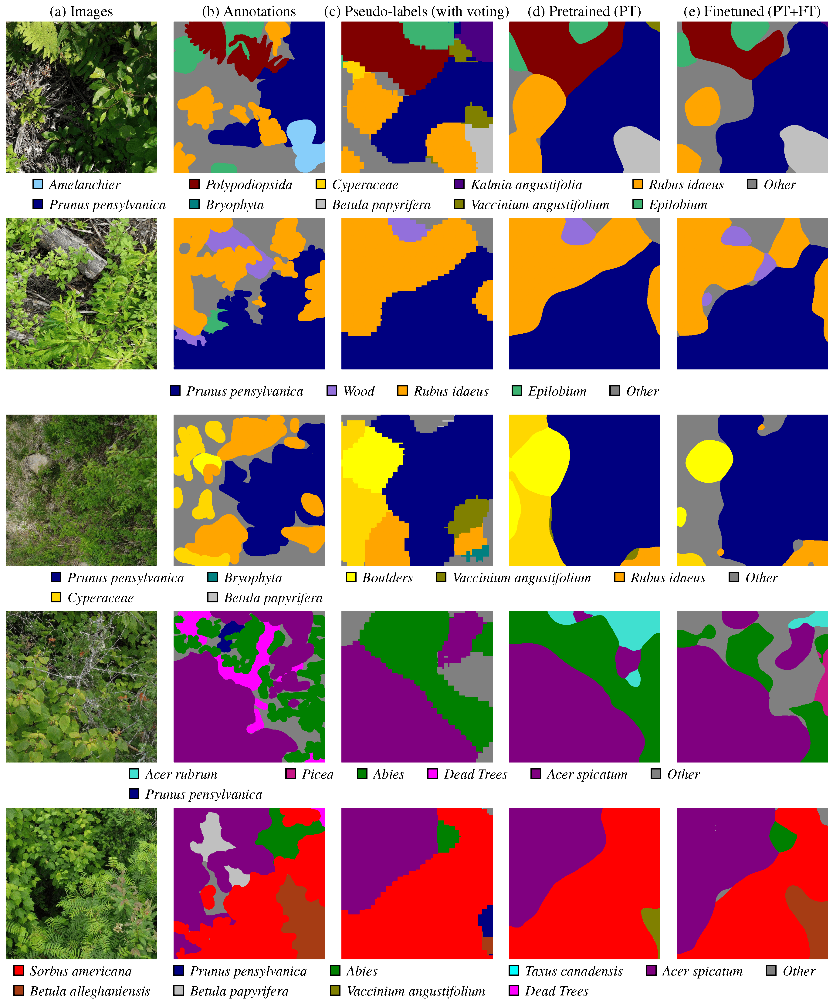

During the last months, I contributed to the paper Using Citizen Science Data as Pre-Training for Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution UAV Images for Natural Forests Post-Disturbance Assessment, published in the Classification of Forest Tree Species Using Remote Sensing Technologies: Latest Advances and Improvements special issue of the Forests MDPI journal. This paper proposes a novel pre-training approach for semantic segmentation of UAV imagery, where a classifier trained on citizen science data generates over 140,000 auto-labeled images, improving model performance and achieving a higher F1 score (43.74%) than training solely on manually labeled data (41.58%). With this paper, we highlight the importance of AI for large-scale environmental monitoring of dense and vasts forested areas, such as in the province of Quebec.
Artificial Intelligence Resources
Learning resources for anyone interested in the vast domain of AI

Here is a slightly curated list of learning resources and useful links in Computer Vision, Artificial Intelligence and related topics. For resources on robotics, visit the robotics resources post. If you have other great resources to suggest, feel free to contact me.